1 1: Define Managerial Accounting and Identify the Three Primary Responsibilities of Management Business LibreTexts

Marginal Costing is another type of managerial accounting that deals with the cost of goods. It involves determining the impact of adding one additional unit of a product to the purchase or production order. Financial accounting is only aimed at keeping historical data about all the financial transactions a company has engaged in. It is responsible for producing financial statements for external use such as balance sheets and income statements. On the other hand, managerial accounting does not have to fulfill any form of general standards. Managerial accounting only has to fulfill internal standards and principles set to achieve business goals.
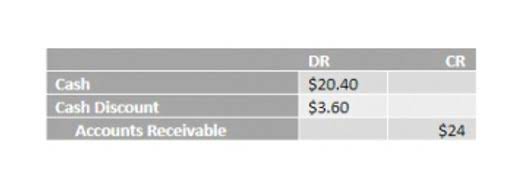
Marginal Costing
- Trend analysis examines historical data to identify patterns and changes over time.
- This includes financial records and accounts about the total cost of goods and services purchased by a company.
- Cost accounting is a large subset of managerial accounting that specifically focuses on capturing a company’s total costs of production by assessing the variable costs of each step of production, as well as fixed costs.
- The financial statements are typically generated quarterly and annually, although some entities also require monthly statements.
- The possible bottlenecks that may occur and their impact on the overall cash flow, revenue, and profit are determined by managerial accountants.
- In managerial accounting, planning involves creating forecasts and budgets that translate the business’ goals and objectives into quantitative information.
This means landing a managerial accounting position will give you an excellent opportunity to impress your team while building valuable skills and relationships. Another example of the accrual method of accounting are expenses that have not yet been paid. Even though the company won’t pay the bill until August, accrual accounting calls for the company to record the transaction in July, debiting utility expense. Work opportunities for a financial accountant can be found in both the public and private sectors. A financial accountant’s duties may differ from those of a self-employed accountant who works for many clients preparing their accounts, tax returns, and possibly auditing other companies. Managerial accounting goes beyond traditional financial reporting to encompass a broader scope that integrates financial and non-financial information.
Common Calculations used in Capital Budgeting:
- While managerial accountants are not the decision-makers, they help drive business decisions based on data and insights.
- The overhead expenses may be allocated based on the number of goods produced or other activity drivers related to production, such as the square footage of the facility.
- By dividing the business into smaller sections, a company is able to get into the details and analyze the smallest segments of the business.
- When conducting differential analysis, the decision makers only include relevant costs.
In this role, they analyze the internal financial processes of an organization and use that data to forecast, make suggestions, aid in decision-making, set budgets, and more. Financial accounting deals with the long-term financial decisions an organization may make. This differs from managerial accounting, which works with short-term and sometimes long-term goals that involve an organization’s internal financial processes.
Cost Accounting:
Costs may be broken down into subcategories, such as variable, fixed, direct, or indirect costs. Cost accounting is used to measure and identify those costs, in addition to assigning overhead to each type of product created by the company. Managerial accounting uses operational information in specific ways to glean information. For example, it may use managerial accounting cost accounting to track the variable costs, fixed costs, and overhead costs along a manufacturing process. Then, using this cost information, a company may decide to switch to a lower quality, less expensive type of raw materials. In the other example, the utility expense would have been recorded in August (the period when the invoice was paid).
Understanding the cause and effects of past bottlenecks can help with policy design and strategic planning. Investopedia is considered to be the largest Internet financial education resource in the world. There are many short, helpful videos that explain various concepts of managerial accounting.
- We can simply refer to cost as the money we pay to suppliers for purchasing goods and services or the money we pay to other parties, such as employees or utility companies, to obtain certain benefits for the business.
- Managerial accounting assesses financial performance and hopes to drive smarter decision-making through internal reports that analyze operations.
- Now that you have a basic understanding of managerial accounting, consider how it is similar to and different from financial accounting.
- Cash flow analysis studies the impact of a single financial decision or transaction to see the true impact of that purchase or decision.
- Because of this, financial accounting procedures are required to fulfill certain standards set by regulatory bodies.
Step #4: Budgeting and Planning
Optimizations can then be made to reduce the possibility or impact of excessive inventory. Cash flow analysis studies the impact of a single financial decision or transaction to see the true impact of that purchase or decision. Financial professionals may look at several options and ways to finance a purchase based on that analysis.


Commentaires récents